1.
F
A current will flow through something only if there is a
___________ across it's ends.
voltage (or potential difference)
2.
F
The bigger the voltage across a circuit, the bigger the
______ that flows through it.
current
3.
F
Resistors slow
down the current going through them - they have _________
resistance
4.
F
the bigger the resistance of something the bigger/smaller
the current
smaller
5.
F
If the resistance of something is large then a
larger/smaller voltage is needed to produce a particular current.
larger
6.
F/H
The p.d. across a component is measured in ________ using a
_________ connected _______ the component.
volts, voltmeter,across (or in parallel with)
7.
F/H
The current flowing through a component in a circuit is
measured in _______ using an _______ connected in _______
Amperes (Amps), ammeter, series
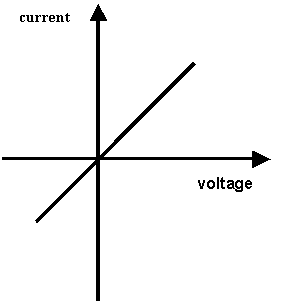
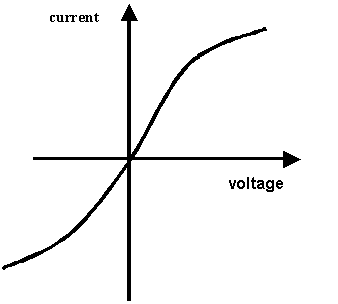
sketch a current / voltage graph for:
A resistor at constant temperature.
A filament lamp.
|
|
|
|
When components are connected in series:
9.
F/H
* their total
resistance is ______________________
the sum of their separate resistances
10.
F/H
* the same /
different current flows through each component (choose)
same
11.
F/H
*
the total voltage of the supply is shared between them - OR they
all have the same voltage (choose)
it's shared
12.
F/H
what is the total resistance of a 200 Ohm resistance in
SERIES with a 300 Ohm resistor?
200 + 300 = 500 Ohms
13.
F/H
Two resistors only are connected in series across a battery
The p.d. across each resistor is 9V What is the voltage of the
battery?
9 + 9 = 18V
14.
F/H
Each of these two resistors have a current flowing through
them of 2A, what is the current flowing out of the battery?
2A
When components are connected in parallel:
15.
F/H
*
there is the same/different voltages across each component
same
16.
F/H
*
the current through each component depends on its resistance OR the
same current flows through each component (choose)
depends on resitance
17.
F/H
*
the total current through the whole circuit is the same in all
aprts of the circuit OR is the sum of the currents through the separate
components (choose)
sum of separates
18.
Just two reistors are connected in parallel - if they each
have a current flowing through them of 2A what is the current flowing out
of the battery?
2 + 2 = 4A
19.
F/H
These two resistors each have a p.d. across them of 9V -
what is the voltage of the battery?
9V
20.
F/H
The potential difference provided by cells connected in
series is the sum of the potential difference of each cell separately TRUE
or FALSE?
TRUE (but it depends upon which way they are connected)
Draw symbols for:
21.
F/H
switch (open)
lamp
switch (closed)
fuse
22.
F/H
cell
voltmeter
battery
ammeter
23.
F/H
Diode
resistor
variable resistor
24.
H
thermistor LDR
 |
25.
H
Write down the formula that connects: Resistance, voltage
and current
resistance = voltage / current
26.
H
A lamp has is connected to 240V and has 2A passing through
it - calculate it's resistance (and show the unit)
res = volt / curr = 240 / 2 = 120 ohms
27.
H
An electric heater has a resistance of 50 ohms.
If it is connected to mains voltage what current flows through it?
res = volt / curr OR curr = volt / res = 240 / 50 = 4.8 A
28.
H
The current through a resistor (at constant temperature) is
proportional to the _______ across the resistor
voltage
29.
H
The resistance of a filament lamp increases/decreases as
the temperature of the filament increases.
increases
30.
H
The current through a diode flows in one direction only
TRUE or FALSE
TRUE
31.
H
A diode has a very low resistance in the reverse direction.
TRUE or FALSE
FALSE it's
high
32.
H
The resistance of a light dependent resistor
increases/decreases as the light intensity/temperature increases.
decreases, light
33.
H
The resistance of a thermistor increases/decreases as the
light/temperature increases.
decreases, temp
34.
F/H
An electric current is a flow of charge/protons/photons
(choose)
charge
35.
F/H
When electricity flows through a resistor, electrical
energy is transferred as _______
heat
36.
F/H
what is the formula that connects power, time and energy?
power = energy/time
37.
F/H
1 watt is what …?
the transfer of 1J of energy in 1s.
38.
A kettle supplies 60000J every minute - calculate its power
power = energy / time (in seconds) = 60000 / 60 = 1000
Watts
39.
F/H
what is the formula that connects power, current and
voltage?
power = voltage x current
40.
A light bulb passes 0.16A when connected to 240V what is
it's power rating?
= 240 x 0.16 = 38.4 W
41.
H
The higher the voltage of a supply, the less/more the
amount of energy transferred for a given amount of charge which flows.
more
42.
H
what is a coulomb?
unit of electrical charge
43.
H
what is the formula that connects charge, current and time?
current = charge / time
44.
H
how does an amp compare to coulombs?
1 amp = 1 coulomb flowing for one second
45.
H
A light bulbs has a current of 2A flowing through it for 10
minutes - what quantity of charges passes through in this time?
curr = charge / time OR
charge = current x time (in seconds) = 2 x 10 x 60 = 1200 coulombs
46.
F
The UK mains supply is about _______ volts
230
47.
F
Most electrical appliances are connected to the mains using
cable and a plug with how many pins?
3 pin plug
48.
F
descibe the inside of the cable - with a reason
two or three inner cores of copper, because copper is a
good conductor;
49.
F
descibe the outside of the cable - with a reason
outer layers of flexible plastic, because plastic is a good
insulator.
50.
F
why does a plug have a plastic or rubber case?
because plastic and rubber are good insulators;
51.
F
why are the pins made of brass?
because brass is a good conductor;
52.
F
name 5 other part of a plug
earth, live, neutral, fuse, cable grip
53.
F
what is the fuse for?
prevent fires, it's a thin wire that melts if too much
current flows through it
54.
F
why do some appliances have an earth wire?
to make any explosed metal parts safe - in case they become
live. Appliances with metal cases are usually earthed.
55.
F
* the blue wire is connected to the______ terminal;
neutral
56.
F
* the brown wire is connected through a ______ to the
______ terminal;
fuse, live
57.
F
* the green/yellow wire (when fitted) is connected to the
______terminal;
earth
58.
F/H
Mains electricity is an a.c./d.c. supply. (choose)
a.c.
59.
F/H
An alternating current (a.c) is one which _________________
is constantly changing direction.
60.
F/H
Mains electricity has a frequency of _______ cycles per
second or ___ h_______
50, 50 Hertz
61.
F/H
Cells and batteries supply a current which always flows in
the same direction. This is called a ____ _______
direct current
62.
F/H
If a fault in an electrical circuit or an appliance causes
too great a current to flow, the circuit can be automaticllay switched off
by a______ or a__________ ____________
fuse, circuit breaker
63.
F/H
The fuse should have a much higher value than the current
through the appliance when it is working normally. TRUE or FALSE?
FALSE - higher, but as close as possible to the current
64.
F/H
When the current through a fuse wire exceeds the current
rating of the fuse the wire becomes ____ and will (eventually) _________
hot, melt
65.
F/H
describe how a circuit breaker works
it can contain an electromagnet, too much current flowing
throught the coils of the electromagnet will attract a switch - which is
set to disconnect the circuit when it is attracted
66.
H
Appliances with metal cases need to be _________The ______
pin is connected to the case via the
_______ coloured wire. If a fault in the appliance connects the case to
the live wire, and the supply is switched on, a very large current flows
to_______ and ______________________________
earthed, earth, green/yellow, earth, overloads or melts the
fuse
67.
H
The live terminal of the mains supply alternates between
a______ and_______ voltage with respect to the neutral terminal. The
neutral terminal stays at a voltage close to ______ with respect to Earth.
positive, negative, zero
68.
F
Much of the
energy transferred in homes
and industry is electrical energy. This is because electrical
energy is readily transferred as:
(chose three four energy forms)
heat (thermal energy), light, sound, movement (kinetic
energy)
describe the main energy changes in:
69.
F
a kettle
electrical --> heat
70.
F
a hi-fi
electrical --> sound
71.
F
a tv
electrical --> sound and light
72.
F
a hairdryer
electrical --> kinetic and heat
name another device that transfers:
73.
F
electrical --> heat
e.g. toaster
74.
F
electrical --> sound
e.g. radio
75.
F
electrical --> sound and light
e.g. computer
76.
F
electrical --> kinetic and heat
e.g. fan heater
77.
F/H
Units of electricity depend upon how long the appliance is
switched on TRUE or FLASE?
TRUE
78.
F/H
Units of electricity depend upon how fast the appliance
transfers energy (its power) TRUE or FALSE?
TRUE
79.
F/H
The power of an appliance is measured in _______ or
__________.
watts, kilowatts (or J/s or kJ/s)
80.
F/H
The amount of energy transferred from the mains is measured
in _________, called Units.
kilowatt-hours
81.
F/H
An electric heater has a power rating of 2kW and is used
for 5 hours - how many units does it consume?
2 x 5 = 10 units
82.
F/H
if a unit costs 7p calculate the cost of using a 10kW
immersion heater for 5 hours
units = 10 x 5 = 50 units cost = 50 x 7p = 350p = £3.50
83.
F/H
If you read your electricity meter in May and it reads
23454 and in March it read 23354 how many units have you used?
23454 - 23354 = 100
84.
F/H
how much would these units cost you at 7p per unit?
100 x 7p = 700p = £7.00
85.
F/H
A ligh bulb has a power of 100W - if it used for 1 minute
calculate the energy supplied
power = energy/time so energy = power x time (in seconds)
= 100 x 1 x 60 = 600Joules
86.
F
When certain different materials are rubbed against each
other they become electrically ________ Electrically ______ objects
attract/repel small objects placed near to them. (choose)
charged, charged, attract
describe the effect of bringing together the following
charged objects:
87.
F/H
(a) a negative ballon and a negative ruler
repel
88.
F/H
(b) a positive duster and a negative tv screen
attract
89.
F/H
(c) a negative tv screen and a nuetral strip of plastic
attract
90.
F/H
oppsoite charges ______
attract
91.
F/H
the same charges _______
repel
92.
F/H
When two different materials are rubbed against each other,
_______, which have a negative charge, are rubbed off one material on to
the other.
electrons
93.
F/H
The material which gains ________ becomes ________ charged;
the material which loses _______ is left with an equal ________ charge.
electrons, negatively, electrons, positive
94.
F/H
When an object becomes positive in charge it gains protons
- true or false?
false - it loses electrons
95.
F/H
describe one example of how electrostatic charges are used
in everyday life.
e.g. photocopier, cling film, used to repel the droplets of
paint or liquid fertilizer out of sprayers, used to remove dust particles
from pollution
96.
F/H
A charged conductor can be _______ by connecting it to the
Earth with a conductor.
discharged
97.
F/H
describe one situation in which static electricity is
dangerous and explain how precautions can be taken to ensure that the
electrostatic charge is discharged safely.
e.g. lightning conductors on the side of tall buildings
98.
F/H
In solid conductors, an electric current is a flow of
_________
electrons
99.
F/H
When some chemical compounds are ______ or dissolved in
______ they conduct electricity.
melted, water
100.
F/H
These compounds are made up of electrically charged
particles called ______
ions
101.
F/H
The current is due to negatively charged_______ moving to
the______ terminal (electrode) and the positively charged ______ moving to
the _____ electrode.
ions, positive, ions, negative
102.
F/H
In the above process simpler substances can be released at
the terminals (electrodes). This process is called __________
electrolysis
103.
H
The greater the charge on an isolated object, the greater
the________ or _________ _______ between the object and the Earth. If the
voltage becomes high enough, a ______ may jump across the gap between the
object and any earthed conductor which is brought near it.
voltage, potential difference, spark
104.
H
Metals are good conductors of electricity because …
some of the electrons from their atoms can move freely
throughout the metal structure.
105.
H
During electrolysis the mass and/or volume of the substance
deposited or released at the electrode increases:
* when the current decreases/increases
increases
106.
H
* when the time for which the current flows descreases/increases.
increases